Team 1: 100% Clean, Renewable Energy
“The Trump administration has already added nearly $40 billion in new federal subsidies for oil, gas, and coal in 2025, …sending an additional $4 billion out the door each year for fossil fuels over the next decade. That new amount, created with the passage of the One Big Beautiful Bill Act this summer, adds to $30.8 billion a year in preexisting subsidies for the fossil fuel industry. The report finds that the amount of public money the U.S. will now spend on domestic fossil fuels stands at least $34.8 billion a year.”
“The cost of turning daytime solar power into reliable anytime electricity has fallen again this year. A new analysis from energy think tank Ember shows that the cost of storing electricity with utility-scale batteries has fallen to just $65/MWh as of October 2025 outside China and the US, meaning that delivering solar when it is needed is now economically feasible.”
Stanford University Professor Mark Z. Jacobson discusses his recently published book, “No Miracles Needed: How Today’s Technology Can Save Our Climate and Clean Our Air.”
Click for article
“Private economic benefit supports a tripling of US heat pump adoption from 11% to 32% of single-family houses.”
Articles
Cities can follow Stanford’s energy makeover to cut emissions of carbon dioxide affordably
Decentralized Microgridding Can Provide 90% of a Neighborhood's Energy Needs, Study Finds
How Utilities Stall Progress On Alternative Energy
Oil And Gas Giants Spend Millions Lobbying To Block Climate Change Policies
Plummeting battery prices to make electric cars cheaper than gas cars in 3 years
Renewable Energy Could Save $160 Trillion In Climate Change Costs by 2050
United States Spend Ten Times More On Fossil Fuel Subsidies Than Education
Why is Norway the Land of Electric Cars? - drive in the bus lane, park and charge for free and get a 25% tax break when you buy an electric car.
Renewable Energy - Geothermal
Iceland's Nesjavellir geothermal power station. Geothermal plants account for more than 25 percent of the electricity produced in Iceland. Photo: Gretar Ívarsson
There are three main ways to use geothermal energy:
Geothermal heat pumps - About 10 feet below the ground, the temperature stays between 50° and 60° F throughout the year. Geothermal heat pumps take advantage of this constant temperature to heat or cool water. By moving water through the ground it can be heated in the winter or cooled in the summer. This water can then be used by a heat exchanger to heat or cool the air in a home. This can be a very efficient and inexpensive way to heat or cool buildings.
Direct use - hot water from hot springs. This water can be used with heat exchangers to heat up homes and buildings. It also can be used to heat pools.
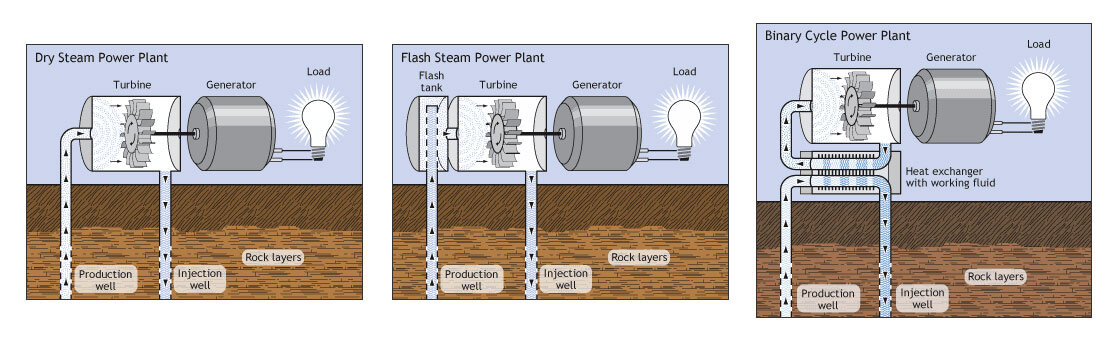
Generating electricity - Geothermal energy can be used by power plants to create electricity. Power plants take advantage of extremely hot water that is between one and two miles deep in the Earth. Some power plants pipe the steam directly up to the generator. They are called dry steam power plants. Other power plants, called flash steam plants, use high pressure from deep in the Earth to create steam to drive the generator.
How Geothermal Energy Works
By Union of Concerned Scientists
How geothermal energy is captured
Geothermal springs for power plants. Currently, the most common way of capturing the energy from geothermal sources is to tap into naturally occurring "hydrothermal convection" systems, where cooler water seeps into Earth's crust, is heated up, and then rises to the surface. Once this heated water is forced to the surface, it is a relatively simple matter to capture that steam and use it to drive electric generators. Geothermal power plants drill their own holes into the rock to more effectively capture the steam.
There are three basic designs for geothermal power plants, all of which pull hot water and steam from the ground, use it, and then return it as warm water to prolong the life of the heat source. In the simplest design, known as dry steam, the steam goes directly through the turbine, then into a condenser where the steam is condensed into water. In a second approach, very hot water is depressurized or "flashed" into steam which can then be used to drive the turbine.
In the third approach, called a binary cycle system, the hot water is passed through a heat exchanger, where it heats a second liquid—such as isobutane—in a closed loop. Isobutane boils at a lower temperature than water, so it is more easily converted into steam to run the turbine. These three systems are shown in the diagrams below.
The three basic designs for geothermal power plants: dry steam, flash steam, and binary cycle. Image: U.S. Department of Energy
Renewable Energy - Solar
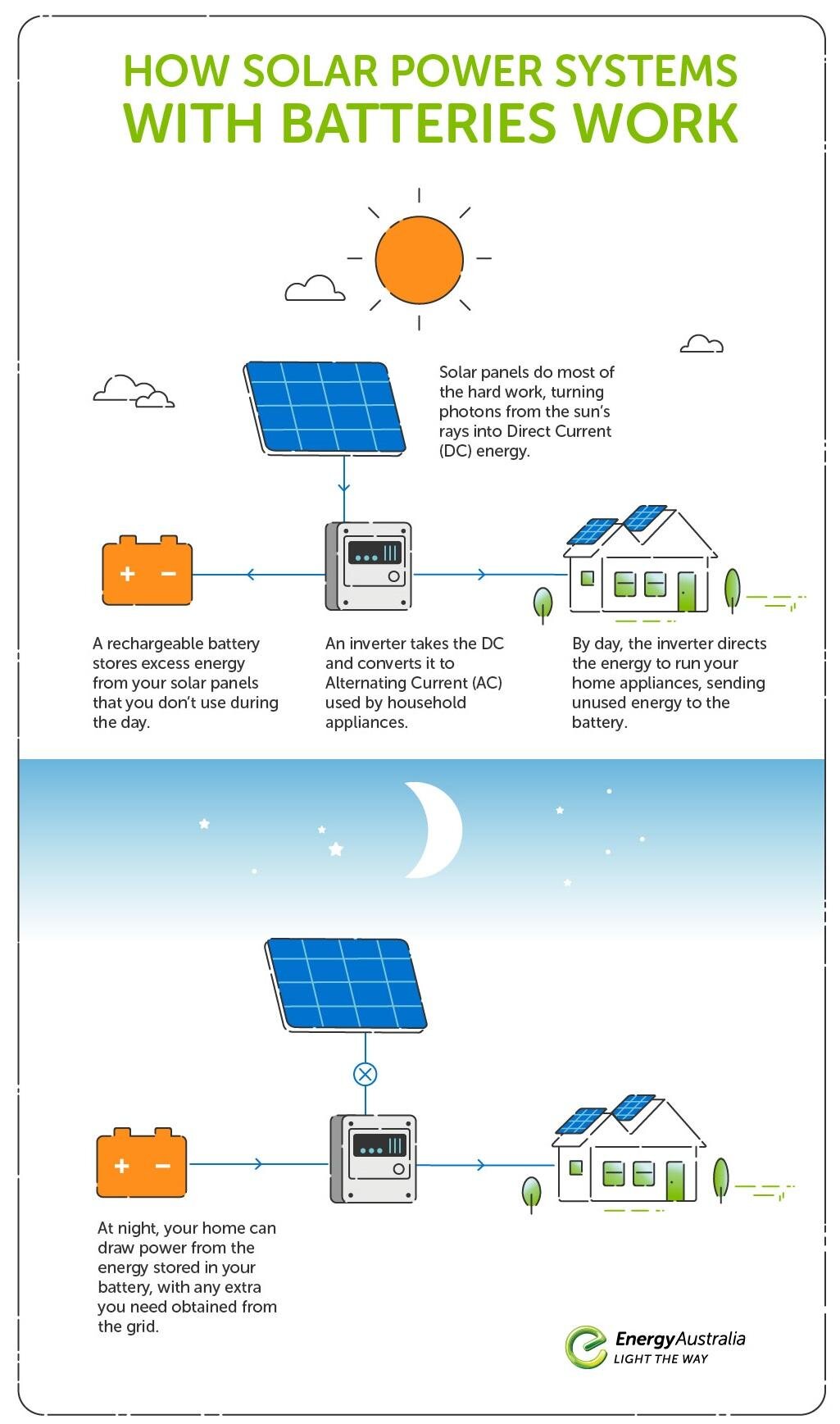
Solar energy is the most abundant energy resource on Earth. Sunlight is converted to electricity with a photovoltaic (PV) solar system which can be used immediately, stored in a solar battery or sent to the electric grid.
“The nearly three-year-long Russia-Ukraine war, which has left large swaths of Ukraine destroyed, has accelerated a transition to clean energy.”
“In centralized systems, all power is generated and sent to the grid over transmission lines from the same area. That means if the plant goes down, say in an attack, a large section of grid, or even the entire grid, comes to a halt. By contrast, wind and solar installations are usually more scattered, so less of the system goes down with one hit, and if the solar is on rooftops, the impact can be even more limited.”
How much solar would it take to power the U.S.?
Escondido high schools shifting to solar power
Large solar farm powering much of Six Flags in New Jersey
Solar Installations in US Now Exceed 2 million
100% Clean Energy School Districts Campaign - how to implement solar in schools
Energy Star for K-12 School Districts
Renewable Energy - Water (Hydroelectric)
Hydroelectric power plants capture the energy of falling water to generate electricity. A turbine and generator convert the falling water into electricity.
Hydroelectric plants range in size from "micro-hydros" that power only a few homes to giant dams that provide electricity for millions of people.
Large dams cause large scale environmental damage because they alter ecosystems, reduce biodiversity, can cause extinction and contribute to climate change because of the massive amounts of concrete and steel used.
Hydroelectric power can be done without this damage by using things like whirlpool turbines and waterwheels.
Renewable Energy - Wind
Wind Energy Basics
Offshore Wind Energy
Combine Wind, Solar and Wave energy generation in a single platform
Renewable Energy - Batteries and Storage
Energy Storage can be divided into categories:
Batteries – energy is stored using electrochemical, including advanced chemistry batteries, flow batteries, and capacitors
Thermal – Thermal energy storage (TES) stores energy by heating or cooling a material (like molten salt, silicon)
Mechanical Storage – use kinetic or gravitational energy to store electricity
Pumped Hydropower – large-scale reservoirs of water to store energy
Batteries give electric power to flashlights, cell phones, cars and even houses. A battery is a type of container that stores energy until it is needed. The energy is stored in chemicals inside the battery. When the battery is used, the chemical energy is changed into electric energy.
Introducing Megapack: Utility-Scale Energy Storage
The Missing Link To Renewable Energy. The Future of Large-scale Batteries
Tesla Battery Researcher is ‘Excited’ About New Battery Tech Developed by the Army
Tesla May Soon Have a Battery That Can Last a Million Miles
Three Large-Scale Energy Storage Technologies That May Hold the Keys to Unleashing an All-Out Renewable Energy Transition
Utility-Scale Energy Storage Will Enable a Renewable Grid
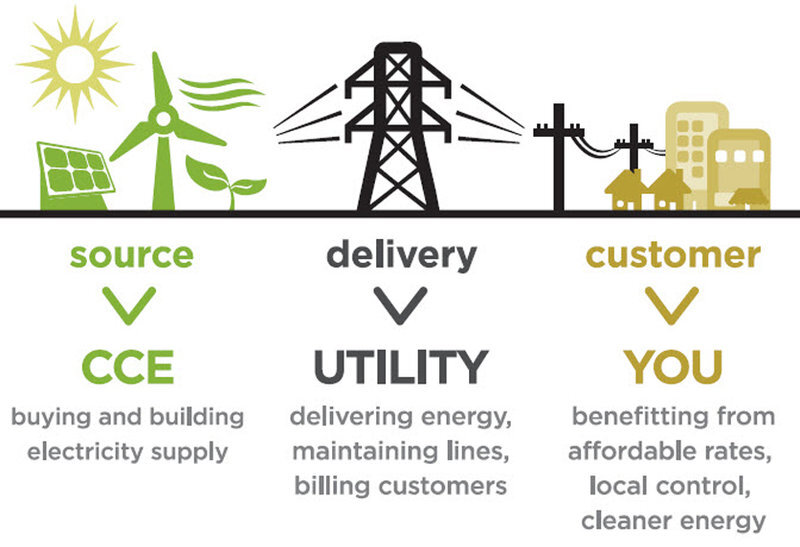
Community Choice Energy (CCE)
What is CCE?
Community Choice Energy, also known as Community Choice Aggregation, is an alternative to traditional investor owned utility (IOU).
California and 9 other states allow cities and counties to establish non-profit electricity providers in order to purchase power on behalf of their residents and businesses and take command of electricity rates. Click here to see if CCE is in your state
The utility company (SDGE, etc.) would continue to operate and maintain the electrical grid, poles & wires and send the monthly bill.
A portion of the payment you make to the utility would be transferred to the new choice provider to pay for the actual power you consume.
It’s a seamless process.
San Diego City Council Approves Community Choice Energy Program.
The San Diego City Council voted to create a JPA (Joint Powers Authority) to buy and sell energy in competition with private companies like San Diego Gas & Electric. The program is key to the city meeting its goals of reducing greenhouse gas emissions.